
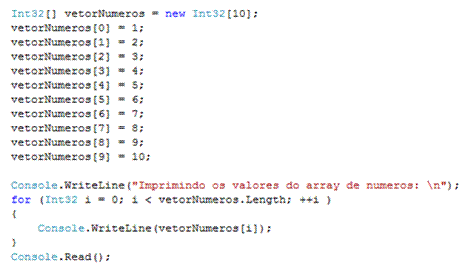
The Length variable is responsible for determining an Array’s length. Here, the objects are incapable of being contained in contiguous locations. They are not able to contain primitives.Īn Array is a native programming component wherein the elements are contained in adjacent memory locations.Īn ArrayList belongs to a class belonging to Java’s collections framework. The add()attribute is utilized for the insertion of elements in an ArrayList.Īn Array can store primitive data types as well as other objects that are of the different or same data type.ĪrrayLists can only store object types. The assignment operator is put to use for the storage of elements. The size of an ArrayList is capable of changing dynamically based on the capacity and load it has to function with. The elements/ items in the data structure can be modified to change the size of the object as and when required.Īs an Array length is static across the program, its size will remain unchanged. The size of the Array cannot be changed once the object has been defined. Array: A comparison chart Basis of DifferentiationĪn array contains a data structure of fixed length.

In this post, we will look into both these data structures in detail and compare them too. Arrays have a fixed length whereas ArrayList has a variable length. In case you have been confused about the difference between Array and ArrayList, then what follows is undoubtedly for you. Both are used for storing elements which can be objects.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
